Proton PEM
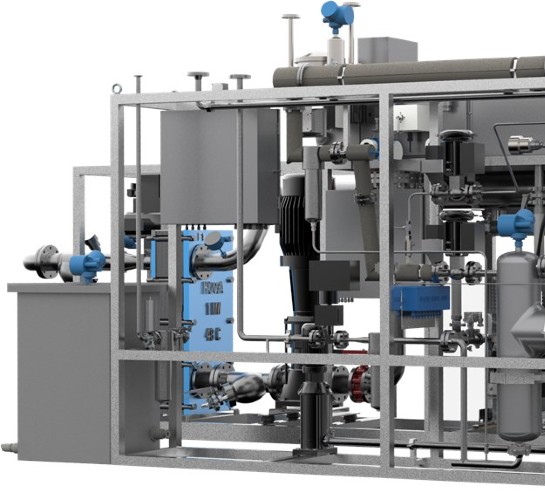
Technical Facts
Flow Range
Gaskon Engineers' provide the following proton hydrogen generator models:-
- C-Series – 10 to 30 nm3/hr
- H-Series – 2 to 6 nm3/hr.
- M-Series – 50 to 400 nm3/hr.
- S-Series – Up to 1 nm3/hr.
Hydrogen Purity
Gakon Engineers' hydrogen generators produce hydrogen with a purity of 99.9995 percent or higher.
Pressure
Proton PEM generators produce very dry gas with a dew point of -65°C or below.
Dew Point
The S-Series and H-Series have a 15-bar standard delivery pressure, whereas the larger C-Series has a 30-bar standard delivery pressure.
How it Works – PSA
A proton exchange membrane electrolysis cell, commonly known as a PME cell, is a device that electrochemically splits water to create hydrogen and oxygen gas using DC power. The cell is called for the electrolyte, it is a type of solid conductive polymer.
In this electrolysis cell, The water enters the note. It is then divided into electrons, protons and oxygen gas. The electrical circuit is bypassed by the protons and electrons that travel through the membrane. At cathode, electrons and protons combine again and create gas of hydrogen. The electrolysis half reactions are shown below.
2H2O→4H++ 4E– + O24H++ 4E–→2H2
The cell has an active region that contains a catalyst that permits the reactions to occur. Membranes that serve as anode and cathode catalysts, as well as anode and cathode flow fields, make up the active area of PEM cells. Each electrolysis cells are built into cell stacks, and the flow feels scatter the flow of reactants, allowing the product to exist in actual implementations.
The anode present in one cell is electrically linked to the cathode of another cell, but they are physically separated. In this approach, the cells are linked electrically in series, while the fluid flows in the stack parallelly. Excess reactant water is often circulated through the cells to cool the electrolysis Tak.

Safety
The alkaline bipolar water electrolysis hydrogen generator designed by the second engineer features extensive monitoring systems to guarantee that the plant runs safely. In the situation of an aberrant operation, the systems are securely depressurized and shut off. The following are a handful of the significant interlocks in our systems. -
- The detection of hydrogen leaks in the plant room.
- The purity of hydrogen.
- The temperature at which the machine operates.
- The H2 generator's operating pressure.
- Purity of oxygen.
- Hydrogen gas dew point.
- The amount of oxygen in hydrogen.
- Water gas for cooling.
- Fault with the rectifier.
- After the hydrogen regulating valve, the pressure is increased.
- Air pressure is measured using an instrument.
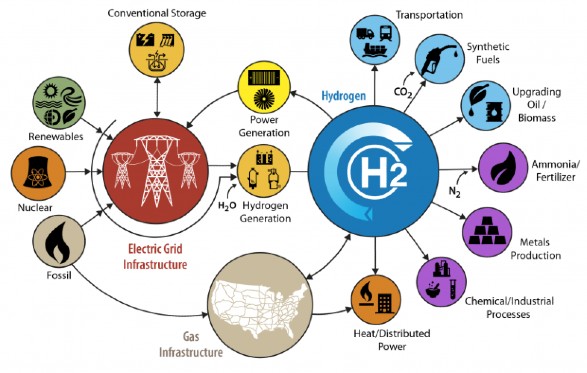
Applications
Water Electrolysis Hydrogen Generators Are Used In:
- Generator cooling in power plants.
- GC stands for gas chromatography.
- Manufacturing of semiconductors.
- The weather balloons are filling up.
- Metallurgical treatment (annealing, brightening, sintering).
- Fats are hydrogenated (food processing).
- The identification of leaks in the air conditioning industry
- Processing of chemicals.
- Pilot plants and refineries
- After the Hydrogen regulating valve, the pressure is increased.
- For the diamond industry, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is used.
Design and Develop by Texmith Infotech . All Rights Reserved













